
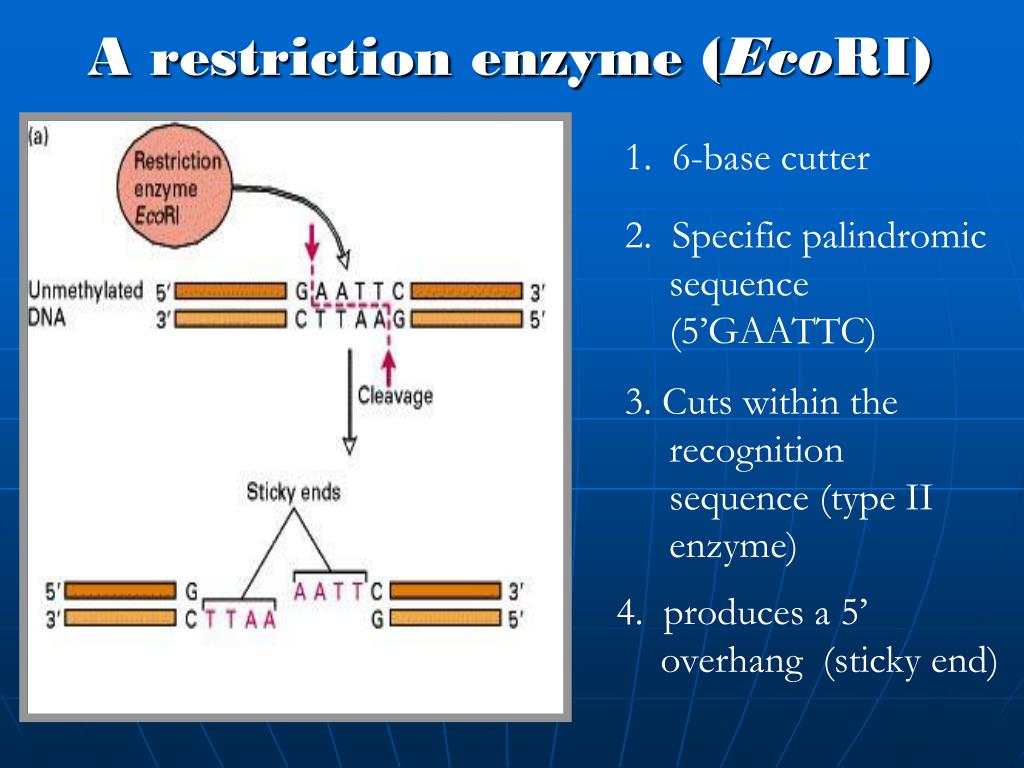
The Specificity of Some Restriction Enzymes Double bars indicate the cleavage site in the DNA strand. A palindromic sequence in DNA is one in which the 5 to 3 sequence is identical on both strands. Restriction enzymes can create fragments with sticky ends, as is the case with the enzyme Bam HI, or blunt ends, as with Hae III ( Table 8.1 ).

Example, GGTCTC (1/5) indicates cleavage at: 5'.GGTCTCN/.3' 3'.CCAGAGNNNN/.5' A HF version of this enzyme is available. Numbers in parentheses indicate the point of cleavage.
#RESTRICTION ENZYME RECOGNITION SITES ARE PALINDROMIC CODE#
Tip: Methylation patterns also differ between different eukaryotes (see bullets above), affecting the choice of restriction enzyme for construction genomic DNA libraries. Generally, the cleavage sites are symmetrically positioned, or palindromic. Enzymes with Nonpalindromic Sequences All recognition sequences are written 5' to 3' using the single letter code nomenclature. Tip: Methylation patterns differ between bacteria and eukaryotes, so restriction patterns of cloned and uncloned DNA may differ. Plant DNA is highly methylated, so for successful mapping in plants, choose enzymes that either do not contain a CpG dinucleotide in their recognition site (e.g., DraI or SspI) or that can cleave methylated CpG dinucleotides (e.g., BamHI, KpnI, or TaqI).Rare-cutter enzymes therefore cleave more frequently in these species.
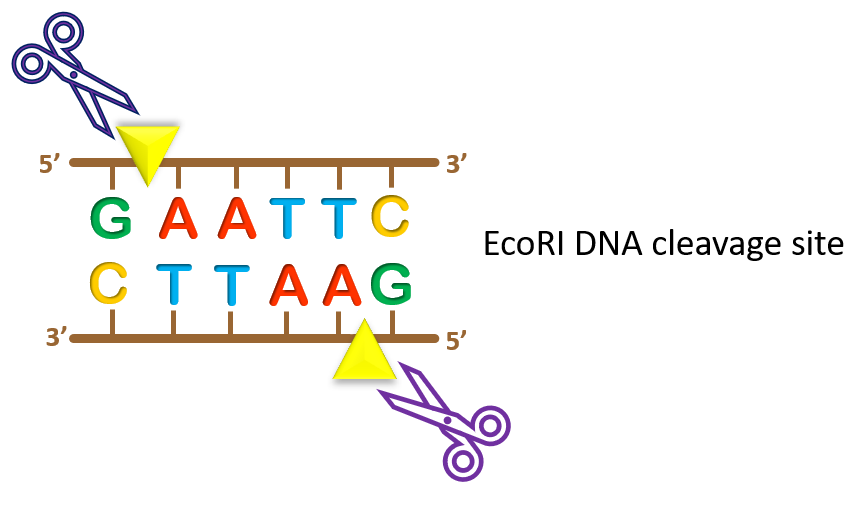
Drosophila, Caenorhabditis, and some other species do not possess methylated DNA, and have a higher proportion of CpG dinucleotides than mammalian species.Therefore many enzymes with CpG in their recognition site, such as EagI, NotI, and SalI, cleave mammalian DNA only rarely. The recognition site for most of the commonly used enzymes is a short palindromic sequence, usually of either 4, 5, or 6 bp in length, such as AGCT (for Alu I), GAATTC (for Eco RI), and so on. The CpG dinucleotide occurs about 5 times less frequently in mammalian DNA than would be expected by chance, and most restriction enzymes with a CpG dinucleotide in their recognition site do not cleave if the cytosine is methylated.In addition, methylation patterns differ in different species, also affecting the choice of restriction enzyme. Therefore the choice of restriction enzyme is affected by its sensitivity to methylation. Not all restriction enzymes can cleave their recognition site when it is methylated. Many organisms have enzymes called methylases that methylate DNA at specific sequences.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
